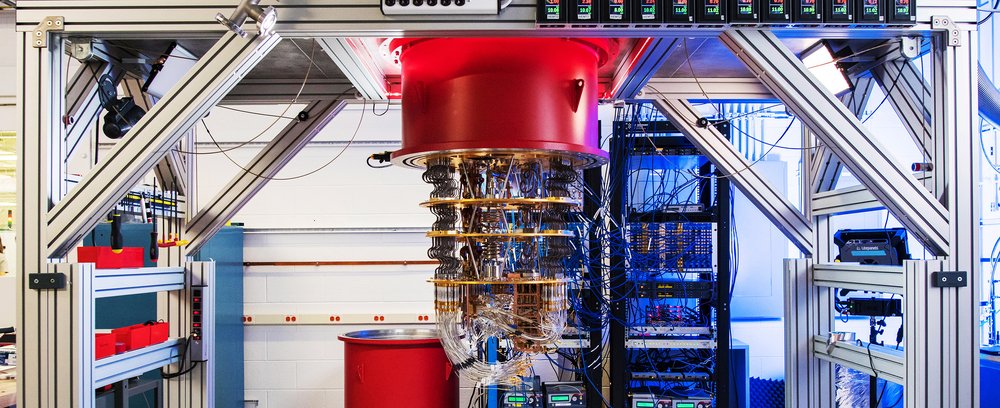
Google’s Quantum AI team has had a productive 2021. Despite ongoing global challenges, we’ve made significant progress in our effort to build a fully error-corrected quantum computer, working towards our next hardware milestone of building an error-corrected quantum bit (qubit) prototype. At the same time, we have continued our commitment to realizing the potential of quantum computers in various applications. That’s why we published results in top journals, collaborated with researchers across academia and industry, and expanded our team to bring on new talent and expertise.
An update on hardware
The Quantum AI team is determined to build an error-corrected quantum computer within the next decade, and to simultaneously use what we learn along the way to deliver helpful—and even transformational—quantum computing applications. This long-term commitment is expanded broadly into three key questions for our quantum hardware:
- Can we demonstrate that quantum computers can outperform the classical supercomputers of today in a specific task?
- Can we build a prototype of an error-corrected qubit?
- Can we build a logical qubit which does not have errors for an arbitrarily long time?

An interactive map of our journey to build an error-corrected quantum computer
Progress toward building an error-corrected qubit prototype
The distance between the noisy quantum computers of today and the fully error-corrected quantum computers of the future is vast. In 2021, we made significant progress in closing this gap by working toward building a prototype logical qubit whose errors are smaller than those of the physical qubits on our chips.

Suppression of logical errors as the number of qubits in the repetition code is increased. As we increase the code size from 5 to 21 qubits, we see 100x reduction in logical. Image acknowledgement: Kevin Satzinger/Google Quantum AI
This year we showed how error decreases as we increase the number of included qubits for a 1-dimensional code. We are currently running experiments to extend these results to two-dimensional surface codes which will correct errors more comprehensively.
Applications of quantum computation
In addition to building quantum hardware, our team is also looking for clear margins of quantum advantage in real world applications. With our collaborators in academia and industry, we are exploring fields where quantum computers can provide significant speedups, with realistic expectations that error-corrected quantum computers will likely require better than quadratic speedups for meaningful improvements.
You can find a list of all our publications here.
Continuing investment in the quantum computing ecosystem
This year, at Google’s annual developer conference, Google I/O, we reaffirmed our commitment to the roadmap and investments required to make a useful quantum computer within the decade. While we were busy growing in Santa Barbara, we also continue to support the enablement of researchers in the quantum community through our open source software. Our quantum programming framework, Cirq, continues to improve with contributions from the community. 2021 also saw the release of specialized tools in collaboration with partners in the ecosystem.
We also released an open-source tool called stim, which provides a 10000x speedup when simulating error correction circuits.
You can access our portfolio of open-source software here.
Looking toward 2022

Resident quantum scientist Qubit the Dog taking part in a holiday sing-along led by team members Jimmy Chen and Ofer Naaman.
Through teamwork, collaboration, and some innovative science, we are excited about the progress that we have seen in 2021. We have big expectations for 2022 as we focus on progressing through our hardware milestones, the discovery of new quantum algorithms, and the realization of quantum applications on the quantum processors of today. To tackle our difficult mission, we are growing our team, building on our existing network of collaborators, and expanding our Santa Barbara campus. Together with the broader quantum community, we are excited to see the progress that quantum computing makes in 2022 and beyond.
Article by Emily Mount. Read full article here.